How to manage dry skin with expert advice, learn about its causes, and understand the ideal skincare routine to keep your skin hydrated.
Introduction
Dry skin is one of the most common skin complaints, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Whether it’s a temporary issue caused by cold weather or a chronic problem linked to certain skin conditions, dry skin can be frustrating, painful, and challenging to manage. The outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis, plays an essential role in keeping moisture in and harmful elements out. When this barrier is compromised or the skin lacks enough natural oils, dryness sets in.
There are multiple reasons why someone may experience dry skin, and understanding those causes is the first step in addressing it effectively. In addition to providing effective treatment options, it’s also important to recognize the significance of prevention. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the science behind dry skin, practical solutions, product recommendations, and lifestyle tips to help you manage this condition with ease.
By the end of this article, you’ll be well-equipped with knowledge about dry skin and how to implement a skincare routine that works for you. Whether you’re dealing with light flakiness or severe dry patches, these expert-backed methods will guide you on your way to soft, smooth, and hydrated skin.
Understanding Dry Skin
To understand dry skin fully, it’s crucial to know what makes it different from other skin conditions like dehydration. Dry skin, or xerosis, is caused by a lack of sebum (natural oils) that the skin needs to stay moisturized. When the skin fails to produce or retain this moisture, it becomes rough, flaky, and may even crack in extreme cases. While dehydration refers to a lack of water in the skin, dry skin refers to the skin’s inability to retain moisture due to a deficiency in oils.
Key Characteristics of Dry Skin
- Rough Texture: The surface of the skin feels rough and sometimes scaly.
- Flakiness: Dry skin often peels or flakes, particularly in areas like the cheeks, elbows, and knees.
- Tightness: The skin can feel tight, especially after washing or exposure to hot water.
- Cracking: In severe cases, the skin may develop visible cracks that can bleed or become painful.
- Itchiness: Dry skin can be intensely itchy, leading to scratching, which further irritates the skin.
Types of Dry Skin
- Temporary Dry Skin: Often caused by environmental factors, such as the weather or exposure to chemicals.
- Chronic Dry Skin: Common in individuals with skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, this form of dry skin requires more focused and long-term care.
- Aging Skin: As we age, our skin’s ability to retain moisture decreases due to reduced oil production, leading to dryness.
Understanding these characteristics allows you to better assess whether your skin issues are seasonal, genetic, or related to an underlying health condition. Knowing how your skin behaves will help you choose the right treatments.
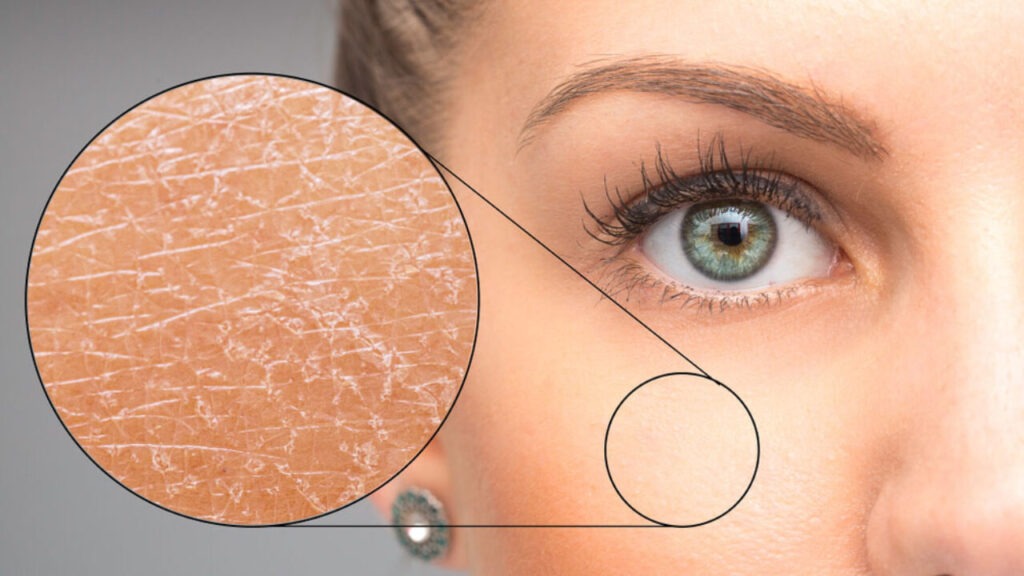
What Causes Dry Skin?
Several factors can lead to dry skin, and it’s important to identify which ones are most relevant to your situation. Dry skin is not just a cosmetic concern—it can be indicative of environmental, lifestyle, or health-related issues. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Environmental Factors:
- Cold Weather: One of the leading causes of dry skin is exposure to cold, dry air. In winter, the humidity levels drop, and the use of indoor heating systems exacerbates the problem. Cold air makes the skin lose moisture quickly, leading to dryness and cracking.
- Low Humidity: Both in winter and in regions with naturally low humidity, the lack of moisture in the air can strip the skin’s moisture barrier, making it difficult to keep the skin hydrated.
- Hot Showers or Baths: While it may feel good to take a long, hot shower, the hot water can strip your skin of natural oils. Prolonged exposure to hot water makes the skin’s moisture barrier more permeable, causing dehydration.
2. Skin Conditions:
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema causes red, itchy patches of skin and is often linked to dry skin. It can be triggered by environmental factors, allergies, or irritation from products. Those with eczema often experience flare-ups of extreme dryness.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition where skin cells rapidly turn over, leading to thick, scaly patches of dry skin. These patches are typically located on the scalp, elbows, and knees.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by an allergic reaction or irritation from substances such as soaps, fragrances, or detergents, contact dermatitis can result in dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
3. Aging:
As we age, the skin’s sebaceous glands produce less oil. The natural oil production decreases, and the skin becomes thinner, drier, and less able to retain moisture. This is why dry skin becomes more common with age.
4. Lifestyle Factors:
- Harsh Skincare Products: Some soaps, cleansers, and lotions are formulated with ingredients that strip the skin of natural oils. Alcohol-based products and those with fragrances can contribute to skin dehydration.
- Diet: A lack of healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, in the diet can contribute to dry skin. Foods like fish, avocados, nuts, and seeds are essential for maintaining the skin’s natural moisture levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the skin’s moisture balance. Stress can also cause the release of cortisol, which has been linked to dryness and inflammation.
5. Medications:
Certain medications can contribute to dry skin. For example:
- Diuretics: Often prescribed for heart conditions, diuretics can lead to dehydration and result in dry skin.
- Retinoids: Common in acne treatments, retinoids can cause dryness and peeling by accelerating cell turnover.
- Antihistamines: These can reduce the moisture levels in the skin, particularly for people who take them regularly for allergies.
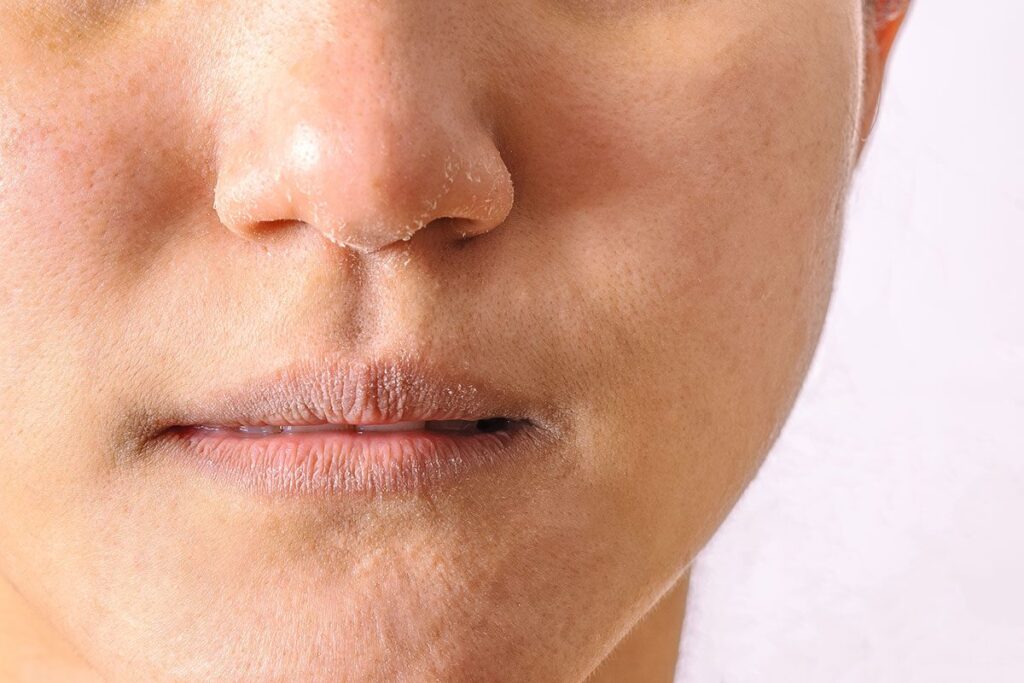
Common Issues Associated with Dry Skin
Dry skin may seem like a minor issue, but if left untreated, it can result in more significant problems. Here are the common issues people face with dry skin:
1. Flakiness and Rough Texture:
Dry skin may appear flaky and feel rough to the touch. This is because the skin cells are not holding enough moisture to maintain a smooth, soft surface. Flakiness is most common on the face, elbows, knees, and hands.
2. Tightness and Discomfort:
Dry skin can feel tight, especially after washing the face or body. This tight feeling is a sign that the skin’s moisture barrier is compromised and moisture is being lost too quickly.
3. Cracking or Fissures:
Severe dry skin can lead to visible cracks or fissures in the skin. These can be painful and may even bleed, making the skin vulnerable to infection.
4. Itching:
Dryness often causes itching, which leads to scratching. Scratching not only makes the itch worse but also damages the skin, which can create more dryness or even infections.
5. Premature Aging:
Chronic dryness accelerates the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Since dry skin lacks moisture and elasticity, it becomes more prone to sagging and lines.
6. Increased Sensitivity:
Dry skin often reacts more sensitively to skincare products, environmental factors, or allergens. It’s common for those with dry skin to experience redness, irritation, and inflammation from triggers like harsh weather or certain skincare ingredients.
Crafting the Ideal Skincare Routine for Dry Skin
A solid skincare routine tailored to dry skin should focus on hydration, nourishment, and creating a protective moisture barrier. The right combination of products and techniques can help you manage dryness effectively.
1. Cleansing:
Cleansing is a crucial first step in any skincare routine. However, when dealing with dry skin, it’s essential to choose the right cleanser.
- Use a Gentle, Hydrating Cleanser: Opt for cream-based or oil-based cleansers that hydrate the skin rather than stripping it. Avoid foaming or harsh cleansers, as they can further dry out the skin.
- Lukewarm Water: Always use lukewarm water when washing your face, as hot water can remove the skin’s natural oils and exacerbate dryness.
- Cleansing Frequency: Avoid over-cleansing, as it can cause further damage. Cleanse your skin twice a day—once in the morning and once at night.
2. Exfoliation:
Exfoliating can help remove dead skin cells and allow your moisturizer to absorb more effectively. However, with dry skin, it’s essential to avoid over-exfoliation.
- Gentle Exfoliants: Use mild chemical exfoliants (AHAs or BHAs) instead of physical scrubs. This will exfoliate without damaging or irritating the skin.
- Exfoliate Once a Week: Since dry skin is more delicate, limit exfoliation to once a week. Over-exfoliating can worsen dryness and irritation.
3. Toning:
Toners are often overlooked, but they are a critical step for dry skin.
- Hydrating Toners: After cleansing, apply a hydrating toner to balance your skin’s pH and add moisture. Look for toners that contain glycerin, aloe vera, or rose water, which help attract and retain moisture.
4. Moisturizing:
Moisturizing is the cornerstone of any dry skin routine.
- Rich, Nourishing Moisturizer: Choose a thick, cream-based moisturizer that locks in moisture and helps repair the skin’s barrier. Look for ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and squalane.
- Apply While Damp: Apply your moisturizer immediately after cleansing or toning while your skin is still slightly damp. This helps to lock in hydration and prevent moisture loss.
5. Sun Protection:
Sunscreen is essential for all skin types, especially dry skin.
- Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Choose a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Opt for a formula that offers hydration in addition to protection.
- Physical Sunscreens: Physical (mineral) sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are gentle on dry skin and less likely to irritate.
6. Treatment Products:
Incorporating serums, oils, or masks can provide an extra boost of hydration and nourishment.
- Hydrating Serums: Look for serums with hyaluronic acid, which can hold moisture in the skin. Other beneficial ingredients include peptides, squalane, and glycerin.
- Face Oils: Consider using face oils like jojoba oil, rosehip oil, or argan oil to restore the skin’s natural oils and enhance hydration.

Weekly Treatments for Dry Skin
While your daily skincare routine is vital, weekly treatments provide an extra layer of care and healing for your dry skin.
- Hydrating Masks: Hydrating face masks can provide deep nourishment to dry skin. Apply a hydrating mask once a week to replenish moisture. Look for masks with ingredients like honey, aloe vera, avocado, or shea butter.
- Overnight Hydrating Treatments: Overnight masks and treatments allow active ingredients to penetrate deeply while you sleep, providing maximum hydration. Choose products with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, vitamin E, or peptides.
- Exfoliation Treatments: Exfoliating once a week can help remove dead skin cells, making your moisturizer more effective. Use mild exfoliants with AHAs (like glycolic acid) or BHAs (salicylic acid) to dissolve dead skin without irritation.
- Steam Treatments: Steaming your face opens pores, helping your skin absorb products more effectively. Add a few drops of essential oils like lavender or eucalyptus to the steam for added skin benefits.
- Nourishing Oils or Serums: Consider applying nourishing oils or serums once a week to restore and repair your skin’s moisture barrier. Oils like argan, marula, or rosehip oil provide essential fatty acids and antioxidants.
5 Tips for Managing Dry Skin
Managing dry skin goes beyond just using the right products. Lifestyle changes and habits can also play a significant role.
- Hydrate from the Inside Out: Drinking enough water is essential for healthy skin. Proper hydration supports the skin’s ability to retain moisture. Aim for at least 8 cups of water a day.
- Avoid Hot Showers: Hot water strips the skin’s natural oils. Opt for lukewarm water for showers or baths to prevent further moisture loss.
- Use a Humidifier: In dry indoor environments, using a humidifier can help maintain moisture in the air, preventing your skin from drying out.
- Wear Protective Clothing: During the winter months, protect your skin from the harsh winds and cold air by wearing gloves, scarves, and hats.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Limit your exposure to harsh chemicals in cleaning products, soaps, and fragrances, as these can exacerbate dryness.
Conclusion
Dry skin can be a persistent issue, but with the right knowledge, products, and habits, you can effectively manage it. A consistent skincare routine, hydration from within, and protection from environmental factors will help keep your skin nourished and moisturized. Whether you’re dealing with temporary dryness or chronic conditions like eczema or psoriasis, these tips will set you on the right path to achieving smooth, healthy skin.
FAQs
Can dry skin be caused by diet?
Yes, a lack of essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals can contribute to dry skin. Ensure a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Is it necessary to exfoliate dry skin?
Exfoliating dry skin is beneficial, but it should be done gently and infrequently to avoid irritating or damaging the skin.
How often should I moisturize my dry skin?
You should moisturize dry skin at least twice a day—once in the morning and once before bed.
Can dry skin lead to premature aging?
Chronic dryness can contribute to fine lines and wrinkles by weakening the skin’s barrier and reducing its elasticity.
What’s the best type of moisturizer for dry skin?
Look for a thick, cream-based moisturizer with ingredients like ceramides, squalane, or hyaluronic acid to lock in moisture.
Can dry skin cause itching?
Yes, dry skin often leads to itching as it becomes more sensitive and irritated. This can be especially true in cold weather or when skin is exposed to harsh soaps and chemicals.
Is it okay to use oils on dry skin?
Yes, oils such as argan oil, jojoba oil, and coconut oil can be highly effective for dry skin as they help lock in moisture and improve the skin’s barrier.
Are there any natural remedies for dry skin?
Yes, natural remedies like aloe vera, honey, oatmeal, and avocado can provide hydration and nourishment to dry skin.
Can air conditioning make my skin dry?
Yes, air conditioning can lower humidity levels in the air, leading to moisture loss from your skin. It’s best to use a humidifier in air-conditioned spaces to help retain skin hydration.
What should I avoid if I have dry skin?
Avoid harsh exfoliants, hot showers, and products containing alcohol, which can strip your skin of its natural moisture.
Can dry skin be a sign of a health condition?
Yes, conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or thyroid disorders can cause chronic dryness. If your skin is persistently dry and irritated, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider.
Does dry skin get worse in winter?
Yes, cold air, indoor heating, and lower humidity levels during winter months can worsen dry skin. It’s important to adjust your skincare routine to suit the season.
How long does it take to see results from treating dry skin?
With consistent moisturizing and care, you can usually see improvements in your skin within a few days to a week.
Can drinking water help with dry skin?
Yes, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps maintain your skin’s moisture levels and overall health.
Are there any skincare ingredients I should look for to treat dry skin?
Look for products with humectants like glycerin, hyaluronic acid, or urea, which help attract moisture to the skin, and occlusives like petrolatum or shea butter that create a barrier to lock it in.

